Phenolic compounds in potatoes found to modulate glycemic response
03/07/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
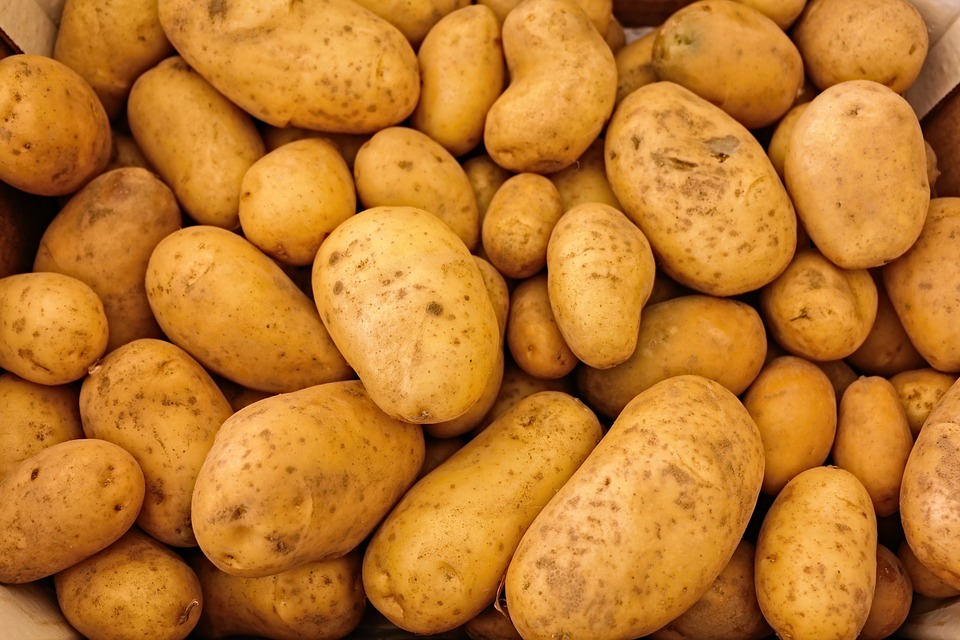

A study shows that phenolic compounds in potatoes may help regulate glycemic response. The study, which was published in the journal Nutrition Research, aimed to determine the phenolic profiles of different varieties of fresh potatoes and chips, as well as to examine the potential of potato phenolic extracts in regulating starch digestion and intestinal glucose transport in model systems.
- A team of researchers at Purdue University used purple-, red-, and white-fleshed fresh potatoes for the study.
- The research team conducted both an in vitro study and a pilot clinical study to examine the differences in glycemic response and gastric emptying between chips from pigmented and white potatoes.
- The results of the in vitro trial showed that potato phenolic extracts of purple, red, and white varieties were high in anthocyanins and chlorogenic acids.
- Potato phenolic extracts did not affect starch digestion, but significantly reduced the rate of glucose transport.
- The results of the clinical study showed that eating purple potato chips modestly but significantly reduced blood glucose at 30 and 60 minutes after consumption compared to white potato chips. However, it did not affect gastric emptying.
In conclusion, these findings suggest that phenolic compounds in fresh potatoes and potato chips may help regulate glycemic response by lowering blood sugar levels.
To read more studies on regulating blood sugar levels, visit BloodSugar.news.
Journal Reference:
Moser S, Aragon I, Furrer A, Van Klinken J-W, Kaczmarczyk M, Lee B-H…Ferruzzi MG. POTATO PHENOLICS IMPACT STARCH DIGESTION AND GLUCOSE TRANSPORT IN MODEL SYSTEMS BUT TRANSLATION TO PHENOLIC RICH POTATO CHIPS RESULTS IN ONLY MODEST MODIFICATION OF GLYCEMIC RESPONSE IN HUMANS. Nutrition Research. April 2018; 52: 57-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.02.001
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
anthocyanins, blood glucose, blood sugar, blood sugar levels, carbohydrate, carbohydrate digestion, Chlorogenic acid, diabetes, diabetics, digestion, food science, fresh potatoes, gastric emptying, glycemic response, phenolic compounds, potatoes, starch, starch digestion
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 DIABETES SCIENCE NEWS