A South American flowering plant is found to have antidiabetic effects
01/24/2019 / By Michelle Simmons

Tietie (Paullinia pinnata), a climbing shrub native to South America and Africa, is rich in antioxidants and can be used to prevent diabetes, according to researchers from Nigeria. This isn’t anything new for local healers, as the plant has been used in folk medicine to treat diabetes-related symptoms. In their study, researchers from the Michael Okpara University of Agriculture investigated the phytochemical composition, antioxidant properties, and anti-diabetes properties of an extract from the root bark of the tietie plant.
For their study, which appeared in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, researchers used mice that had been treated with alloxan to induce diabetes. The mice were then given varying amounts of tietie root bark extract or glibenclamide, an antidiabetic drug.
The researchers found the extract contains alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, tannins, saponins, and sterols. The results of the in vivo test, in particular, revealed that mice treated with tietie root extract exhibited a significant drop in fasting blood glucose levels. The mice were able to better tolerate glucose after being treated with tietie extract, as well as a concentration-dependent increase in antioxidant activity.
Based on their findings, the researchers concluded that tietie root bark has potent anti-diabetes and antioxidant properties. This study also confirmed the use of tietie root bark extract in treating diabetes-related conditions in folk medicine.
Other plants that could help with Type 2 diabetes
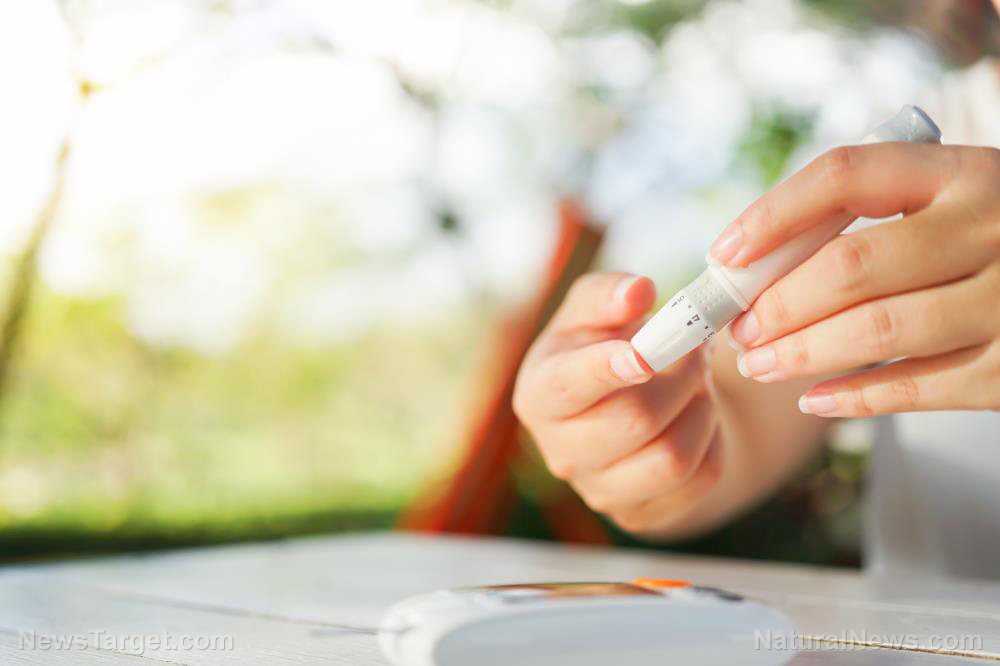
Each day, the number of people getting affected by Type 2 diabetes increases. In the U.S. alone, more than 20 million already have the condition. Because some drug medications for diabetes are not effective and can even cause side effects, researchers continue to search for other treatments for diabetes. Fortunately, there are many herbal supplements that have shown potential in treating Type 2 diabetes.
- Aloe vera: For thousands of years, aloe vera has been used for its therapeutic properties. In the Arabian Peninsula, the dried sap of this plant has been traditionally used to treat diabetes. Some research has found that the juice from the aloe vera plant can help reduce blood sugar in people with Type 2 diabetes. (Related: 16 Powerful Herbs for Diabetes Treatment.)
- Bitter melon: Bitter melon is a widely-known ingredient of Asian cuisine and traditional Chinese medicine. This plant is said to relieve thirst and fatigue, which are possible Type 2 diabetes symptoms. Studies have shown that the extract of bitter melon can lower blood sugar levels.
- Cinnamon: It is believed that consuming about half a teaspoon of this spice each day can lead to great improvement in blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels in people with Type 2 diabetes.
- Curcumin: Curcumin is the main compound of the spice called turmeric. This compound has been shown to improve blood sugar management and also prevent diabetes.
- Fenugreek: Fenugreek is a herb that has been used both as a medicine and as a spice for thousands of years in the Middle East. Human and animal studies have also shown that this herb is effective in regulating blood sugar.
- Ginseng: For more than 2,000 years, ginseng has been used as a traditional medicine. Studies have demonstrated that this herb may lower blood sugar in people with diabetes. Its extract can help regulate blood sugar and enhance insulin sensitivity, according to a study.
- Holy basil: In India, holy basil has been used as a traditional treatment for diabetes. Several studies have also shown that it may improve insulin secretion and cause a positive effect on fasting blood glucose.
Read more news stories and studies on natural diabetes treatments by going to DiabetesScienceNews.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, antidiabetic, antioxidant, diabetes, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, Paullinia pinnata
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 DIABETES SCIENCE NEWS