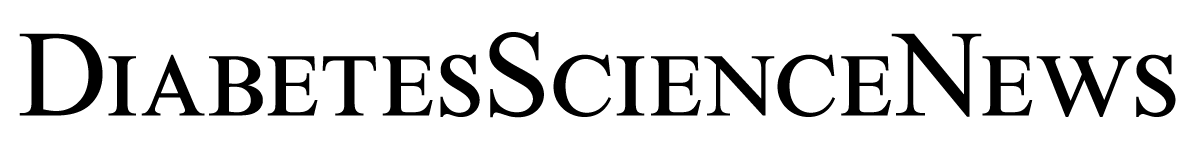Acupuncture found to be a potential adjunct therapy for Type 2 diabetes
07/08/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
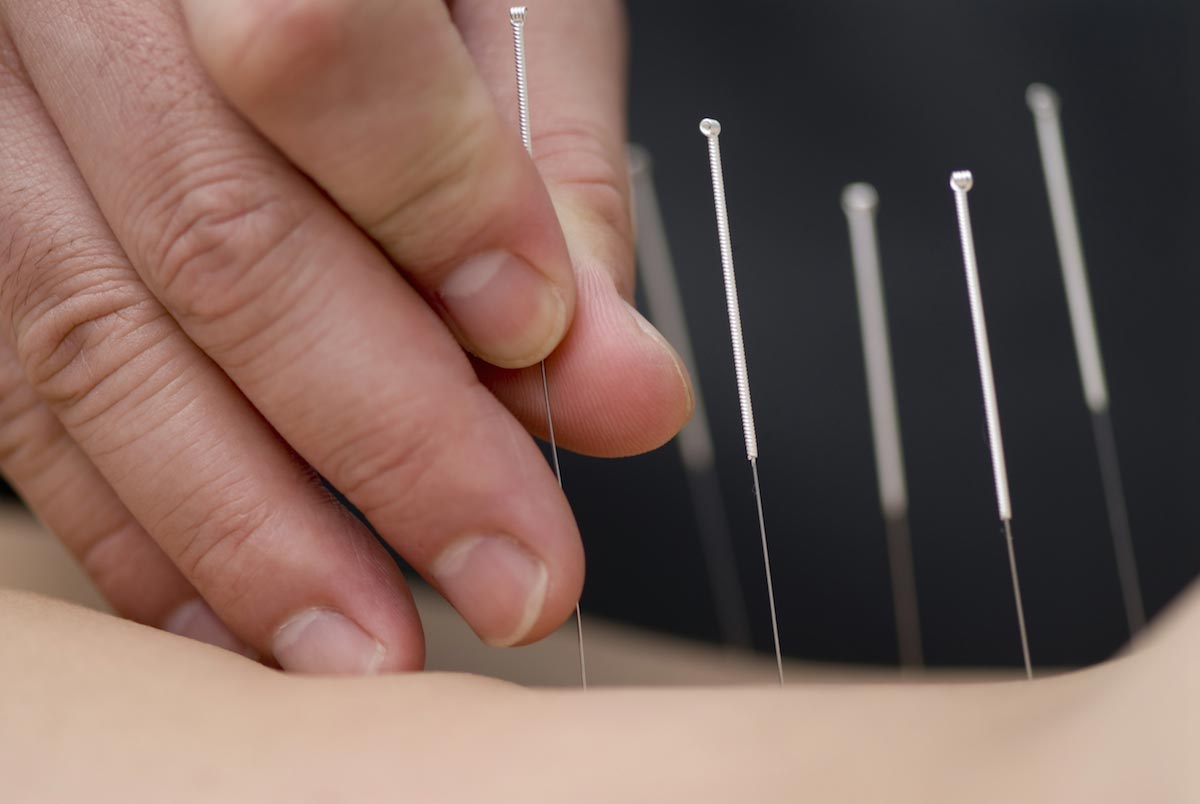
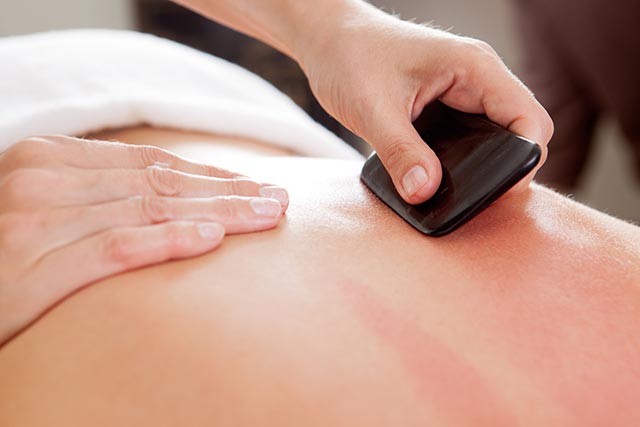
Acupuncture, an ancient technique used to balance the flow or energy, or qi, throughout the body, has been used to treat Type 2 diabetes for 2,000 years. It involves the stimulation of specific points throughout the body to restore the proper flow of qi and activate the body’s natural healing process. Acupuncturists achieve this by inserting tiny, sterile needles into those activation points.
According Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), diabetes can be attributed to three main factors, namely, improper diet, emotional disturbances and constitutional yin deficiency, which is characterized by fatigue, weakness, lethargy and pale complexion. Acupuncture combined with moxibustion is said to be effective for diabetes as they can reduce blood sugar levels and normalize endocrine function.
Indeed, modern research has found that acupuncture can help regulate pancreatic function and insulin levels. Clinical trials also suggest that age-old healing art has anti-obesity effects which can enhance the effectiveness of modern diabetes treatments.
To further explore the effects of acupuncture, researchers at the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences and the World Federation of Acupuncture-Moxibustion Societies conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) involving the use of acupuncture — or any of its variants — as diabetes treatment. They assessed the safety of acupuncture for patients with Type 2 diabetes.
The researchers reported their findings in an article published in the journal Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.
Acupuncture is a safe complementary treatment for the management of diabetes
According to numerous animal studies, the efficacy of acupuncture as diabetes treatment is undeniable. However, researchers have yet to fully explore the effectiveness and safety of this highly regarded TCM technique.
To address this, the researchers systematically searched five databases and two clinical registry platforms from inception until August 04, 2018 for RCTs that involve acupuncture or any of its variants (i.e., oral, scalp, foot, tongue or ear acupuncture).
They selected studies that not only investigated their effectiveness against Type 2 diabetes, but also compared their effects with those of sham acupuncture or no acupuncture controls. Blood sugar control and adverse events were considered as primary outcomes.
The researchers included a total of 21 studies (1,943 participants) in the final meta-analysis. Compared with sham acupuncture or no acupuncture + baseline treatments, the combination of acupuncture and baseline treatments was found to reduce fasting blood sugar, blood sugar levels two hours after drinking a glucose solution and glycated hemoglobin levels. The latter is tested to monitor the long-term control of diabetes.
Besides reducing blood sugar, acupuncture also improved blood lipid levels and blood pressure control and helped reduce the participants’ body weight.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that acupuncture can be used as a supplementary treatment for the management of Type 2 diabetes.
Natural ways to manage your blood sugar levels
Besides acupuncture, there are other simple yet effective ways of reducing your blood sugar without relying on medications. Here are some tips that you can try with or without the acupuncture therapy: (h/t to Healthline.com)
- Exercise regularly. This can help you manage your weight and increase your insulin sensitivity.
- Adopt a low-carb diet. This can help lower your blood sugar and prevent spikes after meals.
- Eat high-fiber foods. Research shows that foods rich in soluble fiber, such as black beans, oats, lentils, chia and flaxseed, can reduce blood sugar levels effectively.
- Drink plenty of water. Staying well-hydrated can help your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine.
- Manage your stress levels. Having high levels of stress hormones can cause your blood sugar to go up. To reduce stress naturally, exercise or practice yoga and meditation.
- Get enough quality sleep. Poor sleeping habits can negatively affect your blood sugar and insulin sensitivity. To improve your sleep quality, develop a healthy sleep hygiene.
- Increase your chromium and magnesium intake. Being deficient in these minerals has been linked to high blood sugar. Incorporate foods like high-bran cereals, nuts, green beans and broccoli into your daily diet to prevent this.
- Try apple cider vinegar. Besides lowering your fasting blood sugar, ACV also improves your body’s response to sugar from your diet.
- Take cinnamon extracts. Studies show that cinnamon slows the breakdown of carbohydrates in the stomach, preventing blood sugar spikes after meals.
- Take berberine supplements. A powerful medicinal plant compound, berberine can help reduce blood sugar if taken regularly.
- Eat fenugreek seeds. An excellent source of soluble fiber, this superfood is great for diabetics aiming to lose weight and improve their blood sugar control.
Healthy lifestyle changes, such as becoming physically active and avoiding high-sugar, high-carbohydrate foods, can help a great deal when it comes to managing symptoms of diabetes. If you wish to combine them with herbal supplements and natural therapies like acupuncture, first consult with a natural health practitioner so you can minimize any risks that might come with your condition or any medication you are taking.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: acupuncture, alternative medicine, Chinese medicine, complementary medicine, diabetes cure, diabetes science, disease treatment, natural cures, natural medicine, Naturopathy, remedies, research
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 DIABETES SCIENCE NEWS